Expanding netmiko-tools
A few months back I created a grep-like utility based on Netmiko. At the time, I wrote an article about that utility including details on specifying the device inventory.
I recently expanded on these netmiko-tools by adding two new utilities: netmiko-show and netmiko-cfg. I would consider these two utilities experimental at this point.Installation
The install process is straightforward. On a Linux system, do the following:
$ pip install netmiko # Requires Netmiko >= 1.0.0
... # output omitted
$ git clone https://github.com/ktbyers/netmiko_tools/
... # output omitted
$ cd netmiko_tools/netmiko_tools/
$ ls
netmiko-cfg netmiko-grep netmiko-show
$ pwd
/home/gituser/EP/netmiko_tools/netmiko_tools
$ export PATH=/home/gituser/EP/netmiko_tools/netmiko_tools:$PATH
$ which netmiko-cfg
~/EP/netmiko_tools/netmiko_tools/netmiko-cfgNote, the netmiko-tools might work on MacOS, but I haven't tested them there. They likely won't work on Windows.
You also have to define an inventory which I detailed here.
At this point, I can check my inventory (which I had previously created):
$ netmiko-show --list-devices
Devices:
----------------------------------------
arista_sw1 (arista_eos)
arista_sw2 (arista_eos)
arista_sw3 (arista_eos)
arista_sw4 (arista_eos)
arista_sw5 (arista_eos)
arista_sw6 (arista_eos)
arista_sw7 (arista_eos)
arista_sw8 (arista_eos)
bad_device (cisco_ios)
bad_port (cisco_ios)
cisco_asa (cisco_asa)
cisco_asa2 (cisco_asa)
cisco_xr2 (cisco_xr)
cisco_xrv (cisco_xr)
hp_procurve (hp_procurve)
juniper_srx (juniper)
pynet_rtr1 (cisco_ios)
pynet_rtr2 (cisco_ios)
Groups:
----------------------------------------
all
arista
asa
cisco
iosxr
junipernetmiko-show
netmiko-show allows you to retrieve show command output from a device or a group of devices. You specify the '--cmd' argument to indicate which command to execute (the default is to retrieve the running-config).
Here are some examples:
/* Single Device */
$ netmiko-show --cmd "show run int fa4" pynet_rtr1
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 146 bytes
!
interface FastEthernet4
description *** LAN connection (don't change) ***
ip address 10.220.88.20 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
end/* Group of Devices */
$ netmiko-show --cmd "show ip int brief" arista
arista_sw1.txt:Interface IP Address Status Protocol MTU
arista_sw1.txt:Management1 unassigned admin down down 1500
arista_sw1.txt:Vlan1 10.220.88.28/24 up up 1500
arista_sw2.txt:Interface IP Address Status Protocol MTU
arista_sw2.txt:Management1 unassigned admin down down 1500
arista_sw2.txt:Vlan1 10.220.88.29/24 up up 1500
arista_sw3.txt:Interface IP Address Status Protocol MTU
arista_sw3.txt:Management1 unassigned admin down down 1500
arista_sw3.txt:Vlan1 10.220.88.30/24 up up 1500
arista_sw4.txt:Interface IP Address Status Protocol MTU
arista_sw4.txt:Management1 unassigned admin down down 1500
arista_sw4.txt:Vlan1 10.220.88.31/24 up up 1500
arista_sw5.txt:Interface IP Address Status Protocol MTU
arista_sw5.txt:Management1 unassigned admin down down 1500
arista_sw5.txt:Vlan1 10.220.88.32/24 up up 1500
arista_sw6.txt:Interface IP Address Status Protocol MTU
arista_sw6.txt:Management1 unassigned admin down down 1500
arista_sw6.txt:Vlan1 10.220.88.33/24 up up 1500
arista_sw7.txt:Interface IP Address Status Protocol MTU
arista_sw7.txt:Management1 unassigned admin down down 1500
arista_sw7.txt:Vlan1 10.220.88.34/24 up up 1500
arista_sw8.txt:Interface IP Address Status Protocol MTU
arista_sw8.txt:Management1 unassigned admin down down 1500
arista_sw8.txt:Vlan1 10.220.88.35/24 up up 1500netmiko-cfg
netmiko-cfg allows you to make config changes from the Linux shell. You can make configuration changes against a single device or a group of devices.
Here are some examples:
/* Verify current config */
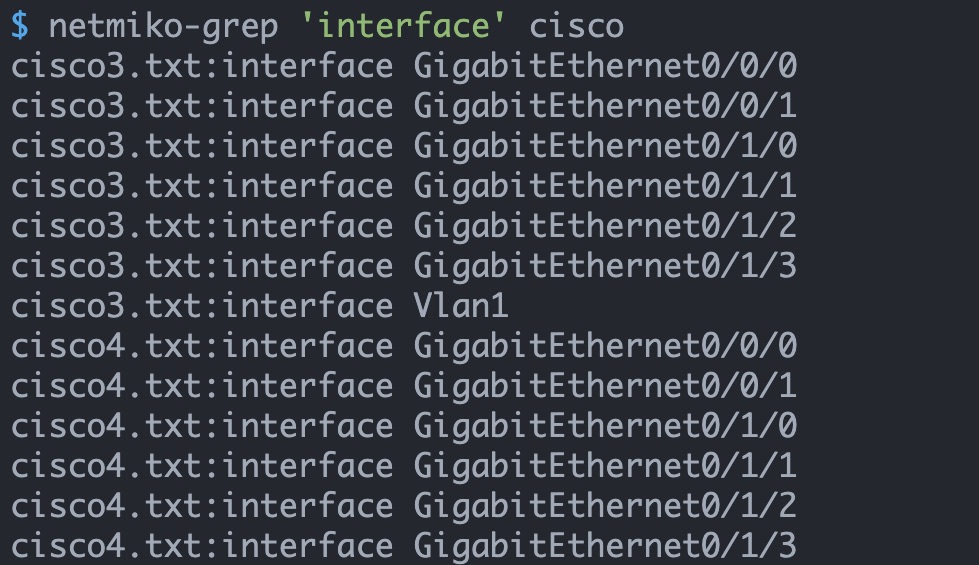
$ netmiko-grep 'logging buffered' cisco
pynet_rtr1.txt:logging buffered 10000
pynet_rtr2.txt:logging buffered 20000 /* Make change to 'cisco' group */
$ netmiko-cfg --cmd 'logging buffer 8000' cisco
pynet_rtr1.txt:config term
pynet_rtr1.txt:Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
pynet_rtr1.txt:pynet-rtr1(config)#logging buffer 8000
pynet_rtr1.txt:pynet-rtr1(config)#end
pynet_rtr1.txt:pynet-rtr1#
pynet_rtr2.txt:config term
pynet_rtr2.txt:Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
pynet_rtr2.txt:pynet-rtr2(config)#logging buffer 8000
pynet_rtr2.txt:pynet-rtr2(config)#end
pynet_rtr2.txt:pynet-rtr2# /* Verify change */
$ netmiko-grep 'logging buffered' cisco
pynet_rtr1.txt:logging buffered 8000
pynet_rtr2.txt:logging buffered 8000You can also feed configuration commands in from a file.
$ cat test_file.txt
ip access-list extended XTEST
10 permit ip host 1.1.1.1 any log
20 permit ip host 2.2.2.2 any log/* Verify ACL isn't configured */
$ netmiko-grep 'XTEST' cisco
$/* Configure ACL */
$ netmiko-cfg --infile test_file.txt cisco
pynet_rtr1.txt:config term
pynet_rtr1.txt:Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
pynet_rtr1.txt:pynet-rtr1(config)#ip access-list extended XTEST
pynet_rtr1.txt:pynet-rtr1(config-ext-nacl)# 10 permit ip host 1.1.1.1 any log
pynet_rtr1.txt:pynet-rtr1(config-ext-nacl)# 20 permit ip host 2.2.2.2 any log
pynet_rtr1.txt:pynet-rtr1(config-ext-nacl)#end
pynet_rtr1.txt:pynet-rtr1#
pynet_rtr2.txt:config term
pynet_rtr2.txt:Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
pynet_rtr2.txt:pynet-rtr2(config)#ip access-list extended XTEST
pynet_rtr2.txt:pynet-rtr2(config-ext-nacl)# 10 permit ip host 1.1.1.1 any log
pynet_rtr2.txt:pynet-rtr2(config-ext-nacl)# 20 permit ip host 2.2.2.2 any log
pynet_rtr2.txt:pynet-rtr2(config-ext-nacl)#end
pynet_rtr2.txt:pynet-rtr2#/* Verify ACL */
$ netmiko-grep 'XTEST' cisco
pynet_rtr1.txt:ip access-list extended XTEST
pynet_rtr2.txt:ip access-list extended XTESTFinally, you can pipe commands in from stdin:
$ echo "no ip access-list extended XTEST" | netmiko-cfg --infile - cisco
pynet_rtr1.txt:config term
pynet_rtr1.txt:Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
pynet_rtr1.txt:pynet-rtr1(config)#no ip access-list extended XTEST
pynet_rtr1.txt:pynet-rtr1(config)#end
pynet_rtr1.txt:pynet-rtr1#
pynet_rtr2.txt:config term
pynet_rtr2.txt:Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
pynet_rtr2.txt:pynet-rtr2(config)#no ip access-list extended XTEST
pynet_rtr2.txt:pynet-rtr2(config)#end
pynet_rtr2.txt:pynet-rtr2#Other things to note:
All of the netmiko-tools create files in ~/.netmiko/tmp. These files store the output of the commands. The files are not automatically removed after execution so you need to be aware of this from a security perspective.
netmiko-tools automatically uses threads for concurrency. netmiko-grep was tested concurrently on 1200 devices and it took between sixty to ninety seconds to complete.
You can find the Netmiko Tools here.
Kirk Byers