Netmiko4 Feature:
send_multiline_timing()

Introduction
I have been working for quite a while developing new features in Netmiko4. Over time, I will be introducing these features to you.
One feature I recently created is send_multiline. Code for this feature is in Netmiko's develop branch and Netmiko4 itself should be released to PYPI early in 2022.
There are two parts to send_multiline: the first is pattern based and the second is timing based. Since the timing based solution is easier, I am going to introduce you to this one first.
The Problem
First, what is the problem we are trying to solve?
There are many situations in network automation where you send a given command down the channel and the network device prompts you for additional information. As a relatively simple example, say you delete a file on a Cisco IOS-XE device, then the CLI interaction would look like this:
cisco3#delete flash:/my_file.txt
Delete filename [my_file.txt]?
Delete bootflash:/my_file.txt? [confirm]y
cisco3# So you send a command down the SSH channel: "delete flash:/my_file.txt" and the router prompts you for additional information (basically asking you twice if this is what you really want to do).
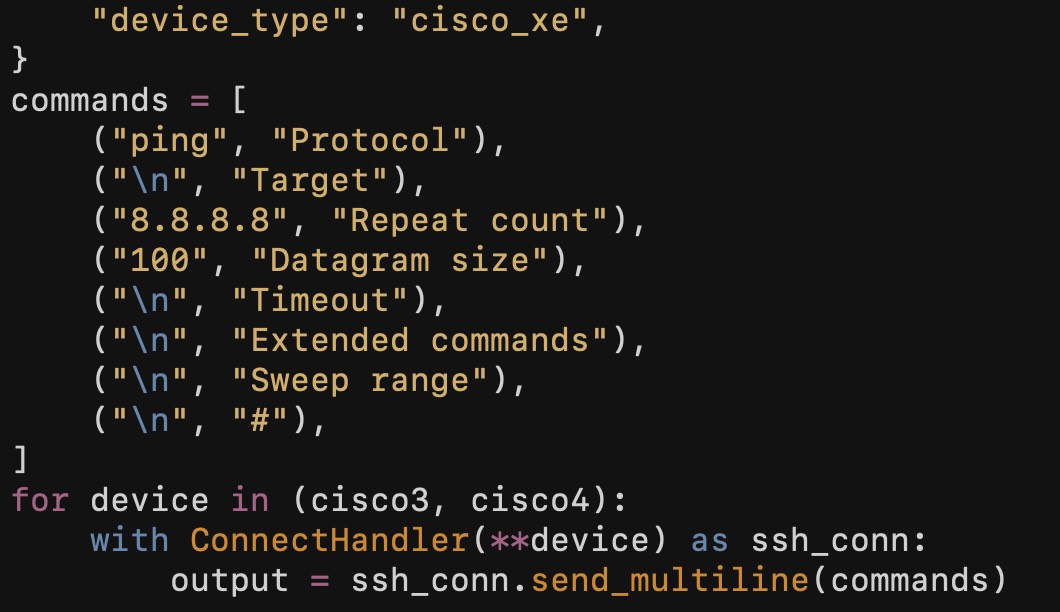
A more difficult example of this multiline prompting would be extended ping on Cisco IOS-XE. Here I type ping and hint <enter> and get a whole series of questions:
cisco3#ping
Protocol [ip]:
Target IP address: 8.8.8.8
Repeat count [5]: 30
Datagram size [100]:
Timeout in seconds [2]:
Extended commands [n]:
Sweep range of sizes [n]:
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 30, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 8.8.8.8, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (30/30), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/4 ms
cisco3# The Netmiko 3.X Solution
Now there are various ways to solve this problem in Netmiko 3.X with typical solutions using a series of either send_command() or send_command_timing() calls.
With send_command() you would send a command down the channel and then specify an "expect_string" (i.e. a pattern) that you were searching for. With send_command_timing() you would similarly send a command down the channel, but then you just wait for some time gathering output (before moving on).
Here is an example executing extended ping using the old Netmiko 3.x solution:
with ConnectHandler(**device) as net_connect:
cmd = "ping"
target_ip = "8.8.8.8"
count = "30"
output = net_connect.send_command_timing(
cmd, strip_prompt=False, strip_command=False
)
output += net_connect.send_command_timing(
"\n", strip_prompt=False, strip_command=False
)
output += net_connect.send_command_timing(
target_ip, strip_prompt=False, strip_command=False
)
output += net_connect.send_command_timing(
count, strip_prompt=False, strip_command=False
)
output += net_connect.send_command_timing(
"\n", strip_prompt=False, strip_command=False
)
output += net_connect.send_command_timing(
"\n", strip_prompt=False, strip_command=False
)
output += net_connect.send_command_timing(
"\n", strip_prompt=False, strip_command=False
)
output += net_connect.send_command_timing(
"\n", strip_prompt=False, strip_command=False
)
print(output)It works, but is cumbersome.
The Netmiko 4.X Solution
So what does the new solution look like:
with ConnectHandler(**device) as net_connect:
filename = "test-bp.txt"
# List of commands
cmd_list = [
f"del flash:/{filename}",
"\n",
"y"
]
output = net_connect.send_multiline_timing(cmd_list)
print(output)So instead of having a series of send_command_timing() calls, we replace that with a list of commands. We then call send_multiline_timing() and pass in our list.
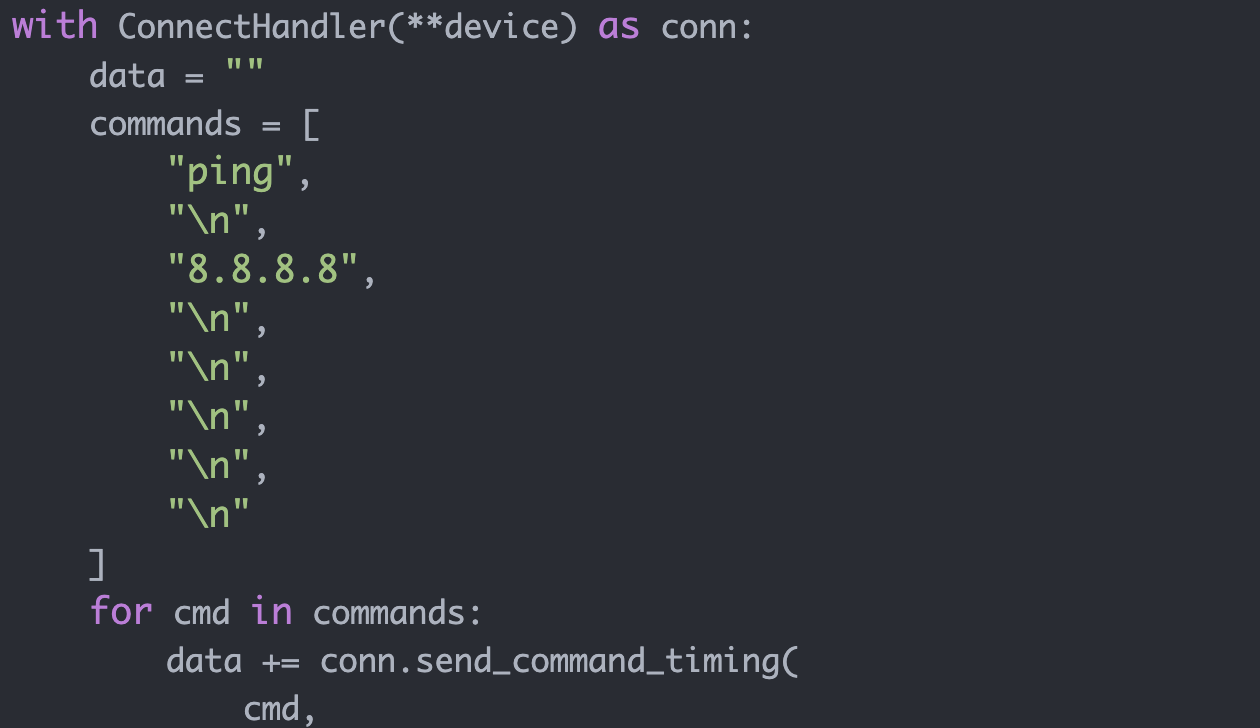
Similarly, you could accomplish the extended ping using the following Python code:
with ConnectHandler(**device) as net_connect:
target_ip = "8.8.8.8"
count = "30"
cmd_list = [
"ping",
"\n",
target_ip,
count,
"\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"\n",
]
output = net_connect.send_multiline_timing(cmd_list)
print(output)The positive for this new solution is that it is simpler syntactically and more intuitive. One negative, however, is that it is a bit slow (especially in the case where you are sending a lot of commands in your cmd_list). In typical situations, it will probably take a little bit more than two seconds per command.
This slowness can be overcome by using a pattern-based solution i.e. send_multiline() which I will talk about in my next article.
Kirk Byers